Brain Bee 脑科学竞赛笔记
Brain Bee 脑科学竞赛笔记
提示
考完试啦! 笔记可能暂停更新了
警告
各位各位 文章中的有些链接是Wikipedia上的 需要魔法才能打开
Table of Contents
脑基础
大脑的结构 Brain Structure
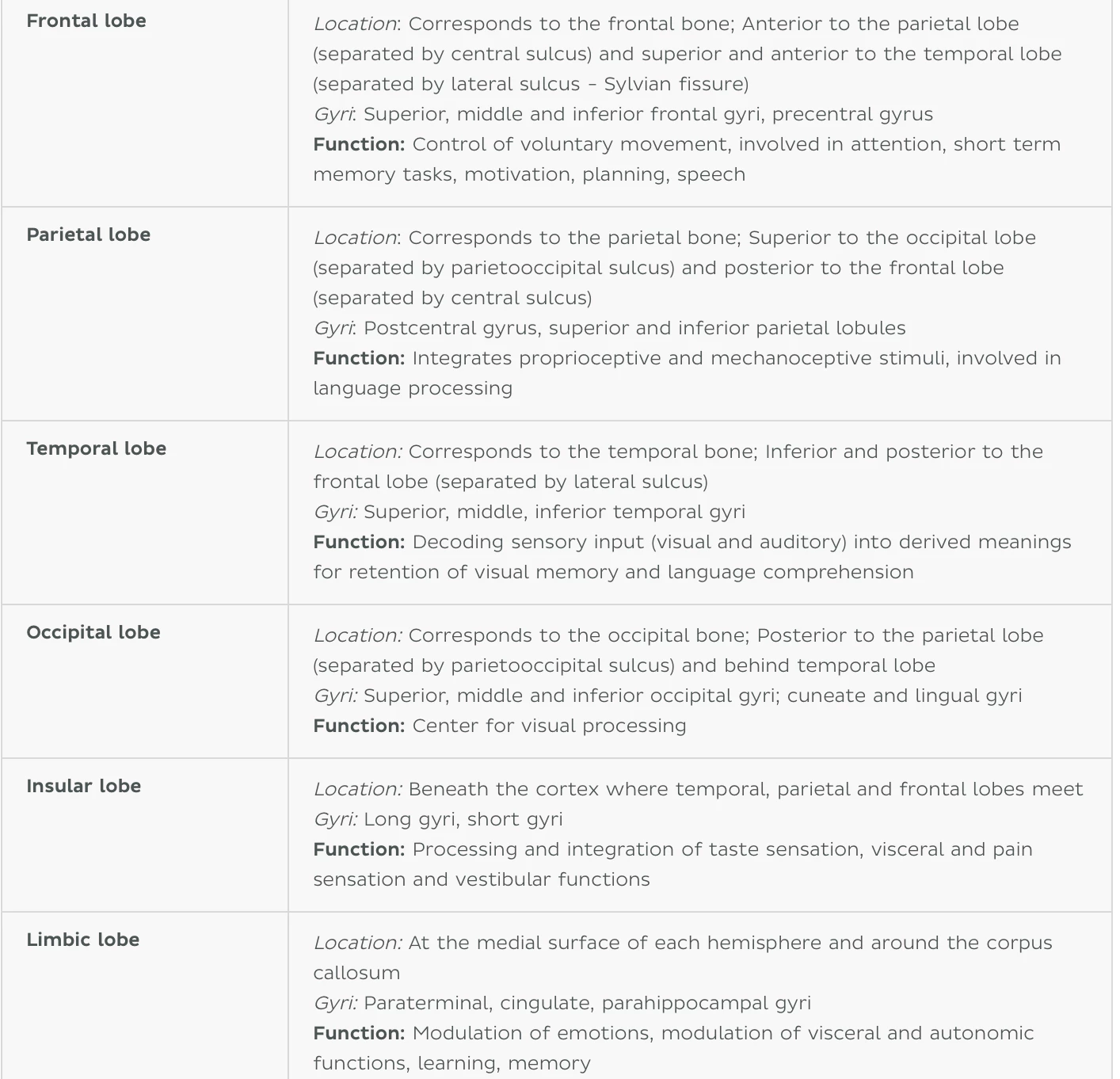
大脑皮层分区
运动皮层
Brodmmans分区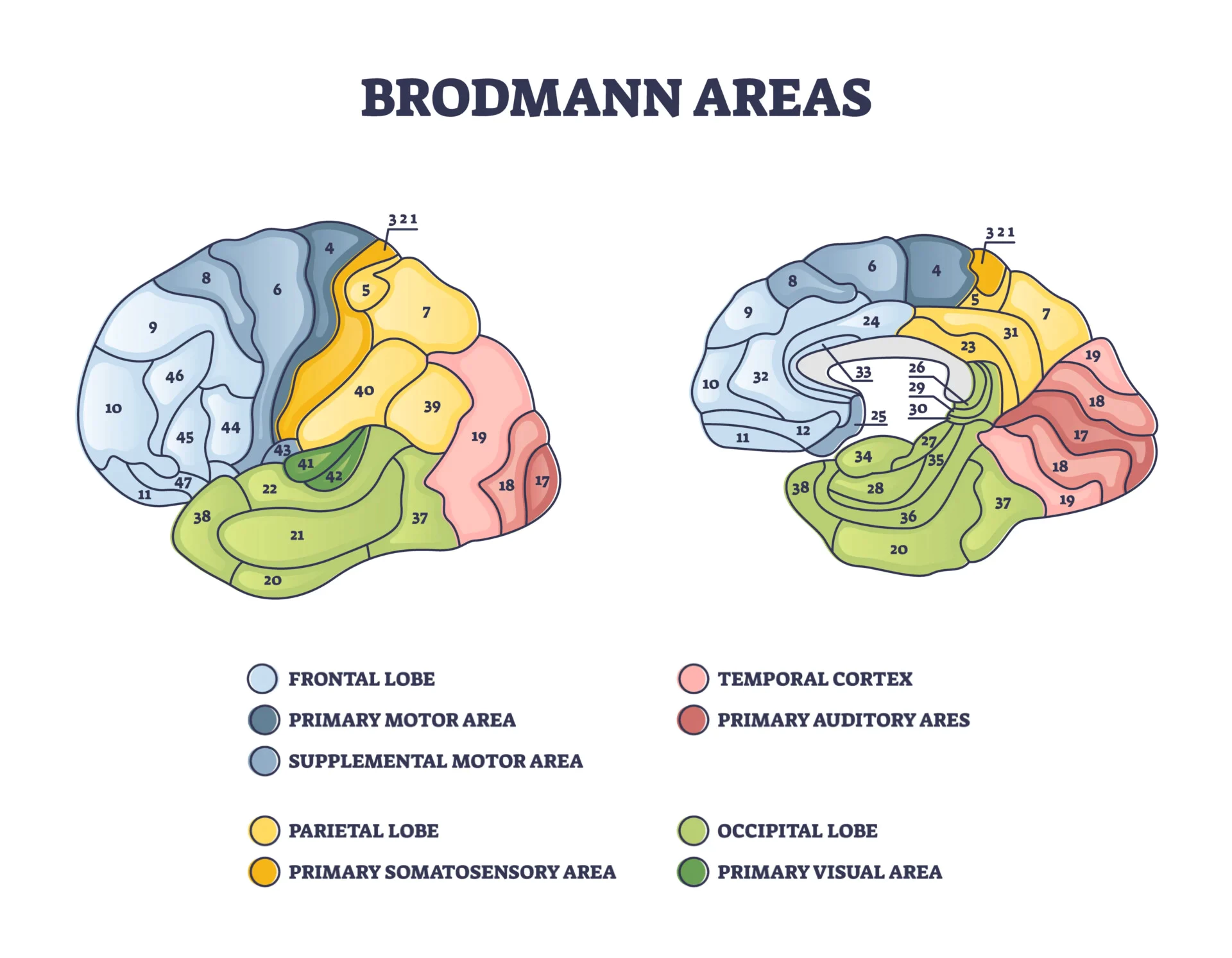
Brodmmans分区
| Brodmann areas | Name | 中文名 | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Somatosensory Cortex | 体感皮层 | Somatic sensory sensations |
| 2 | Same to above | 同上 | Same to above |
| 3 | Same to above | 同上 | Same to above |
| 4 | Primary Motor Cortex | 初级运动皮层 | Motor execution |
| 5 | Somatosensory Association Cortex | 体感联合皮层 | Spatial orientation, among other parietal associational functions |
| 6 | Pre-Motor and Supplementary Motor Cortex | 前运动皮层 | Motor planning and execution |
| 7 | Somatosensory Association Cortex | 体感联合皮层 | Spatial orientation, among other parietal associational functions |
| 8 | Includes Frontal Eye Field | 包括额叶眼动区(Frontal eye field) | Governance of eye movements (contains "frontal eye fields") |
| 9 | Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex | 背外侧前额叶皮层 | Prefrontal associational integration |
| 10 | Frontopolar area (most rostral part of superior and middle frontal gyri) | 额极区(上额回和中额回最前侧的部分) | Same to above |
| 11 | Orbitofrontal area (orbital and rectus gyri, plus part of the rostral part of the superior frontal gyrus) | 眶额区(眶回,直回和上额回前侧的一部分) | Same to above |
| 12 | Orbitofrontal area (used to be part of BA11, refers to the area between the superior frontal gyrus and the inferior rostral sulcus) | 眶额区(上额回和下前回之间的区域) | Same to above |
| 13 | Insular cortex | 脑岛 | Associational cortex |
| 17 | Primary Visual Cortex | 初级视皮层 | Visual information |
| 18 | Visual Association Cortex | 视觉联合皮层 | Same to above |
| 19 | Visual Association Cortex | 视觉联合皮层 | Same to above |
| 20 | Inferior Temporal gyrus | 颞下回 | Same to above |
| 21 | Middle Temporal gyrus | 颞中回 | Processing visual information, among other temporal associational functions |
| 22 | Superior Temporal Gyrus, of which the rostral part participates to Wernicke's area | 颞上回,其前侧部分属于韦尼克区 | Auditory processing and language reception |
| 23 | Ventral Posterior cingulate cortex | 腹后扣带皮层 | Participates in limbic associational integration |
| 24 | Ventral Anterior cingulate cortex | 腹前扣带皮层 | Emotional and cognitive processing |
| 25 | Subgenual cortex | 膝下皮层 | Prefrontal associational integration |
| 26 | Ectosplenial area | 压外区(Ectosplenial area) | Limbic associational integration |
| 28 | Posterior Entorhinal Cortex | 后内嗅皮层 | Olfaction and hippocampal processing |
| 29 | Retrosplenial cingular cortex | 压后扣带皮层 | Limbic associational integration |
| 30 | Part of cingular cortex | 扣带皮层的一部分 | Same to above |
| 31 | Dorsal Posterior cingular cortex | 背侧后扣带皮层 | Limbic and parietal associational integration |
| 32 | Dorsal anterior cingulate cortex | 背侧前扣带皮层 | Emotional and cognitive processing |
| 34 | Anterior Entorhinal Cortex (on the Parahippocampal gyrus) | 前嗅皮层,位于海马旁回 | Olfaction and hippocampal processing |
| 35 | Perirhinal Cortex (on the Parahippocampal gyrus) | 旁嗅皮层,位于海马旁回 | In hippocampal associational functions |
| 36 | Parahippocampal cortex (on the Parahippocampal gyrus) | 海马旁皮层 | Visual and hippocampal associational functions |
| 37 | Fusiform gyrus | 梭状回 | Visual recognition |
| 38 | Temporopolar area (most rostral part of the superior and middle temporal gyri | 颞极区 | Limbic associational integration |
| 39 | Angular gyrus, part of Wernicke's area | 角回,韦尼克区的一部分 | Processing language, spatial orientation and semantic representation |
| 40 | Supramarginal gyrus part of Wernicke's area | 缘上回,韦尼克区的一部分 | Spatial orientation and semantic representation |
| 41 | Primary Auditory Cortex | 初级听觉皮层 | Auditory information |
| 42 | Primary Association Cortex | 听觉联合皮层 | Same to above |
| 43 | Subcentral area (between insula and post/precentral gyrus) | 中央下区(Subcentral area) | Sensorimotor representation and taste processing |
| 44 | Pars opercularis Broca's area | 岛盖部,布洛卡区的一部分 | Language production and participates in prefrontal associational integration |
| 45 | Pars triangularis, part of Broca's area | 三角部,布洛卡区的一部分 | Language production |
| 46 | Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex | 背外侧前额叶 | Participates in prefrontal associational integration |
| 47 | Inferior prefrontal gyrus | 额下回 | Same to above |
| 48 | Retrosubicular area (a small part of the medial surface of the temporal lobe) | 下脚后区,颞叶内侧的一小部分 | |
| 52 | Parainsular area (at the junction of the temporal lobe and the insula) | 脑岛旁皮质 |
额叶 Frontal Lobe
介绍
管理个性、行为、情感,判断、计划和解决问题,演讲:演讲和写作(布罗卡区),身体运动(motor strip),智力、注意力、自我意识等
知乎
额叶(Frontal Lobe)是脊椎动物的脑的一部分,位于脑的前半部(顶叶前方、颞叶上方),在人类大脑当中,比起其余脑中的“叶”,这是最大的一部分,而有些动物的脑几乎不存在额叶。
这个结构和人类语语言的形成、语言表达(布洛卡区)、自主意识以及随意肌的控制有关。
- 管理
- 行走等行为的运动皮质
- 各种行为之间的抉择
- 控制、压制不道德行为
- 判断当前行为的后果
- 整合自边缘系统输入而产生的情绪
损伤
- 无法对情景做出合理反应
- 虚构症
- 二重性记忆错误
临床案例
“As a child, H.M. developed a severe, difficult-to-treat form of epilepsy. When traditional therapies didn’t help, H.M. underwent an experimental surgical treatment — the removal of the medial regions of his temporal lobes. The surgery worked in that it greatly alleviated the seizures, but it left H.M. with severe amnesia. He could remember recent events for only a few minutes and was unable to form explicit memories of new experiences. For example, after talking with him for a while and then leaving the room, upon returning, it would be clear that H.M. had no recollection of the exchange.”
顶叶 Parietal Lobe
管理语言翻译,文字,触觉、疼痛、温度(感觉条),解释来自视觉、听觉、运动、感觉和记忆的信号,空间和视觉感知
The parietal lobe is the center of the somatic senses. Most importantly, this part of the brain plays a significant role in identifying objects around us. Namely, it helps us understand spatial relationships, and correctly analyze and compare the position of one body concerning another or the observer himself. This lobe is also important for pain and touch interpretation.
- 管理
- 中央后回后外侧区
- 空间感(分析相对位置)
- 中央沟后部(中央后回)的初级躯体感觉皮层区
- 痛觉与触觉
- 优势半球顶叶中部
- 语言理解
- 书写能力
- 左右分辨
- 手指辨别
- 非优势半球顶叶
- 解释感官 包括 温度、视觉、感觉、听觉、记忆和运动中枢信号以及视知觉
- 中央后回后外侧区
损伤
- 触觉的解析能力受损
- 侧肢体的病变(病感失认)
- 格斯特曼综合症 GSS
格斯特曼综合症 (Gerstmann’s syndrome)
症状 慢性进行性小脑共济失调,伴有痴呆、构音障碍和脑内淀粉样蛋白沉积,多为家族性
诊断 组织病理学检查、免疫学检查、动物接种试验、物理检查与分子生物学检查
枕叶 Occipital Lobe
枕叶是大脑皮层的一部分,位于枕叶叶轴区域,负责视觉信息的处理和解释。
枕叶位于一个三角形中,其顶点是顶叶和大脑颞叶的两侧。
知乎
枕叶参与视觉处理。它处理和解释我们看到的一切,同时还负责分析一些外部属性,例如形状、颜色和运动,最后解释和总结关于我们看到的图像。
- 管理
- 视觉分析 (Area 17, 18)
- 评估我们所看到的事物的价值 (Area 19)
- 信息的视觉、听觉和一般敏感性 (部分Area 39)
枕叶与边缘系统(尤其是海马体)、顶叶和颞叶有很强的联系。
损伤
- 患者无法通过视觉识别物体
- 癫痫发作也会导致视觉幻象(多为对侧视野上的线条和彩色网格
颞叶 Pariental Lobe
Wikipidea
颞叶是初级和次级听觉皮层的所在地,为处理听觉讯息的中枢。
掌管
- 语言功能 (韦尼克区)
韦尼克区 Wernicke's Area
主要功能 主要掌管语言理解。位于大脑优势半球的颞上回、颞中回后部、缘上回,传统理论上位于布罗德曼分区系统的第22分区,现代理论还包括第40分区。韦尼克区以德国神经学家、医生卡尔·韦尼克的名字命名。
损伤 严重的感觉性失语症。患有该症的患者能够听见声音,但无法理解语言的意思;患者能组织语法上正确的句子,但没有能力在句子中表达任何意义。
- 长期记忆 (海马体)
海马体 Hippocampus
主要功能 大脑边缘系统的一部分,位于大脑皮质下方,担当着关于短期记忆、长期记忆,以及空间定位的作用。海马体中的位置细胞与内嗅皮层中的网格细胞在脑部进行空间定位和导航中扮演重要角色。
损伤 表现症状为记忆力衰退以及方向知觉的丧失。阿尔兹海默症的患者首先收到的损伤也是海马体,具体表现为海马发生肿大,趋向于模式完成,而不是编码新信息,导致记忆障碍会肿大。炎症也会导致海马体受损。
- 听觉与视觉记忆
损伤
- 言语障碍
- 语言障碍
- 记忆力衰退
- 方向知觉的丧失
- 癫痫会导致
- 幻觉 (幻触, 幻嗅, etc)
- 心率加快
- 即视感, 犹昧感
岛叶 Insular Lobe
注意
有的学者认为岛叶是颞叶的一部份。值得注意的是,岛叶是大脑最
掌管
分区
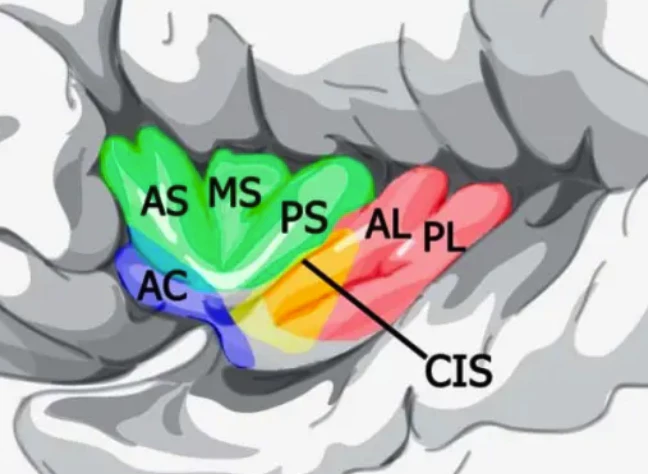
Insular Lobe - 红色 感觉运动
- 黄色 化学感觉
- 蓝色 社会情绪
- 绿色 认知
内脏感觉、自主神经控制和内感
疼痛
听觉加工
前庭功能(平衡)
损伤
- 岛叶损伤的中风病人出现严重的动力下降、烟瘾减弱甚至消失等症状
- 单侧岛叶损伤的病人表现出显著的认知控制容量的损伤
边缘叶 Limbic Lobe
边缘皮层是大脑很重要的一个区域。
Wikipedia
边缘皮层是哺乳动物大脑半球内侧面的一处弧状大脑皮层,也包含了额叶、顶叶和颞叶的部分区域[1][2]。边缘叶是边缘系统的主要部ss分,最初由法国科学家保罗·布罗卡于1878年命名
神经元 Neuron
结构
| A | B | C | D | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细胞核 Nuclues | 细胞体 Soma | 树突 Dendrites | 轴突 Axon | 髓鞘 Myelin | 突触 Synapse |
| 包含遗传物质 | 包括细胞器, 支撑细胞 | 接受动作电位 | 发出动作电位 | 传播动作电位 | 与其他神经元沟通 |
细胞体
Wikipedia
In cellular neuroscience, the soma (pl.: somata or somas; from Greek σῶμα (sôma) 'body'), perikaryon (pl.: perikarya), neurocyton, or cell body is the bulbous, non-process portion of a neuron or other brain cell type, containing the cell nucleus.
- 也创造了细胞运作所需的电位
树突
Wikipedia
A dendrite (from Greek δένδρον déndron, "tree") or dendron is a branched protoplasmic extension of a nerve cell that propagates the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. Electrical stimulation is transmitted onto dendrites by upstream neurons (usually via their axons) via synapses which are located at various points throughout the dendritic tree.
- 获取来自其他神经元的动作电位
- 直接连接突触
轴突
Wikipedia
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences) is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon.
髓鞘
Wikipedia
Myelin (/ˈmaɪ.əlɪn/ MY-ə-lin) is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's electrical wires) to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) pass along the axon.[1][2] The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Rather, myelin ensheaths the axon segmentally: in general, each axon is encased in multiple long sheaths with short gaps between, called nodes of Ranvier. At the nodes of Ranvier, which are approximately one thousandth of a mm in length, the axon's membrane is bare of myelin.
- 包裹着轴突
- 每一段距离会有一个兰氏结(Node of Ranvier), 大概长度为
突触
| 编号 | 名称 | 功能(带*表示与神经科学无关) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 线粒体 Mitochondria | 提供能量 |
| B | 激酶 Kinase | 戳我* |
| C | 突触小泡 | 携带/重摄取神经递质 |
| D | 通道 | 控制神经递质的释放 详情戳我 |
| E | 受体 Receptor | 与神经递质结合 |
| F | ER内质网 | 戳我* |
| G | 活跃区 Active Zone | 释放神经递质的地方 |
| H | 突触后致密区 PSD | 突触后膜胞质面聚集的一层均匀而致密的物质 细胞支架特化结构 |
| I | ??? Reserve Receptors | 我也不清楚🤷但貌似是备用的受体? |
电位
注意
下面的图都是因为我找不到合适的图自己画的 真的很累 要用记得表明出处 谢谢啦
首先先来一些术语
- 电势(电压) 电荷之间形成的势能, 记作. 神经科学里可以想作细胞膜外离子和膜内形成的势能
- 电流 电荷的流动, 记作. 神经科学里可以想作离子的流动
- 电阻 妨碍电流的任何东西, 记作. 神经科学里可以想作细胞膜对于离子流动的阻碍性能
欧姆定律
然后就是动作电位的形成过程了(以下所有电势都是内部相对外部的)
- 静息电位 Resting Membrane Potential 约为 -70 mV, 由Na离子与蛋白质形成
- 这种状态下, 神经元被称为极化(polarized)
- 钠-钾泵分布在细胞的磷脂层上
- 对于每三个送出胞外的Na会往胞内内输送两个K离子, 以保证电化学梯度Electrochemical Gradient
- 神经元的细胞膜上还分布着离子通道
- 有不同种类的离子通道
- 电压门控通道 Voltage-Gated Channels 比如钠通道, 会在大概 -55mV的电势的时候打开
- 配体门控通道 Ligand-Gated Channels 比如乙酰胆碱受体通道, 在和乙酰胆碱配对后打开
- 机械门控通道 Mechanically-Gated Channels 比如压力感受性钠离子通道, 当细胞膜因为梯度导致的应力被撑开, 这玩意也会被拉开
- 电位分为
- 左边 分级电位 没啥用
- 右边 动作电位 会传给下一个神经元
神经递质 Neurotransmitter
神经递质主要分为一下类型:
| 氨基酸 | 单胺类 | 神经肽 | 其他 |
|---|---|---|---|
GABA | 多巴胺 | 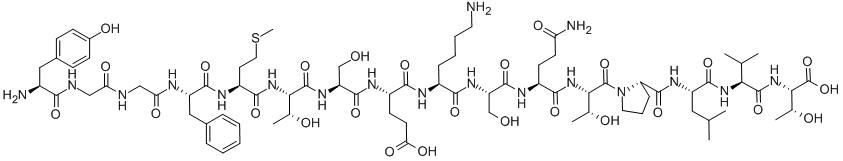 内啡肽(图为alpha-内啡肽) | |
谷氨酸 | 血清素 | ||
甘氨酸 |
- 神经递质是否为兴奋/抑制取决于受体
肽键
若基团与被肽键连接,则
肽
一串被肽键连在一起的氨基酸。也就是蛋白质片段。
乙酰胆碱
Wikipedia
中枢及周边神经系统中常见的神经传导物质,于自主神经系统及体运动神经系统中参与神经传导。乙酰胆碱由轴突末梢释出之后,会穿过突触间隙和突触后神经元或运动终板的细胞膜上之受体结合。
- 平滑肌 兴奋
- 心跳 抑制
受体
在骨骼肌中和N受体(烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体)结合
Wikipedia
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle, and many other tissues of many organisms. At the neuromuscular junction they are the primary receptor in muscle for motor nerve-muscle communication that controls muscle contraction. In the peripheral nervous system: (1) they transmit outgoing signals from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, and (2) they are the receptors found on skeletal muscle that receive acetylcholine released to signal for muscular contraction. In the immune system, nAChRs regulate inflammatory processes and signal through distinct intracellular pathways.[1] In insects, the cholinergic system is limited to the central nervous system.
在平滑肌和M2受体(蕈毒碱型乙酰胆碱受体)结合
Wikipedia
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other cells. They play several roles, including acting as the main end-receptor stimulated by acetylcholine released from postganglionic fibers in the parasympathetic nervous system.
阿兹海默症的人群ACh水平普遍低下
多巴胺
调节类神经递质,主要在中脑中分泌。掌管奖励系统
- 控制动作
- 保证清醒
帕金森综合症人群普遍多巴胺水平低下
精神分裂症人群多巴胺水平过高,导致幻觉
去甲肾上腺素
从肾上腺中分泌
- 加快心跳 兴奋作用
- 减缓肠胃肌肉蠕动 抑制作用
- 掌管唤醒
交感神经系统中主要的神经递质
和肾上腺素受体结合
肾上腺素
- 掌管战逃反应 兴奋作用
- 也是一种激素
和肾上腺素受体结合
γ-氨基丁酸
Wikipedia
GABA is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system.
用于去除神经系统中的噪声 帮助睡眠
低水平的GABA会导致失眠
会被树突和轴突同时分泌
由谷氨酸合成
血清素
又名5-羟色胺
大脑中主要的单胺类神经递质
- 传输内脏感觉 调节作用
低水平的血清素会导致 - 脑雾
- 神智不清
普遍在抑郁/焦虑人群中血清素水平会很低
甘氨酸
- 在CNS中是抑制神经递质
- 假如甘氨酸受体被激活,通过离子接受器进入神经细胞导致抑制性突触后电位
- 和谷氨酸一样的是激动剂
谷氨酸
大脑中最多的氨基酸
主要为兴奋神经递质
和NMDA(N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体)受体或者AMPA(α-氨基-3-羟基-5-甲基-4-异恶唑丙酸)受体结合
会直接影响神经可塑性,帮助学习
催产素
这这这 结构简式写不下啊(悲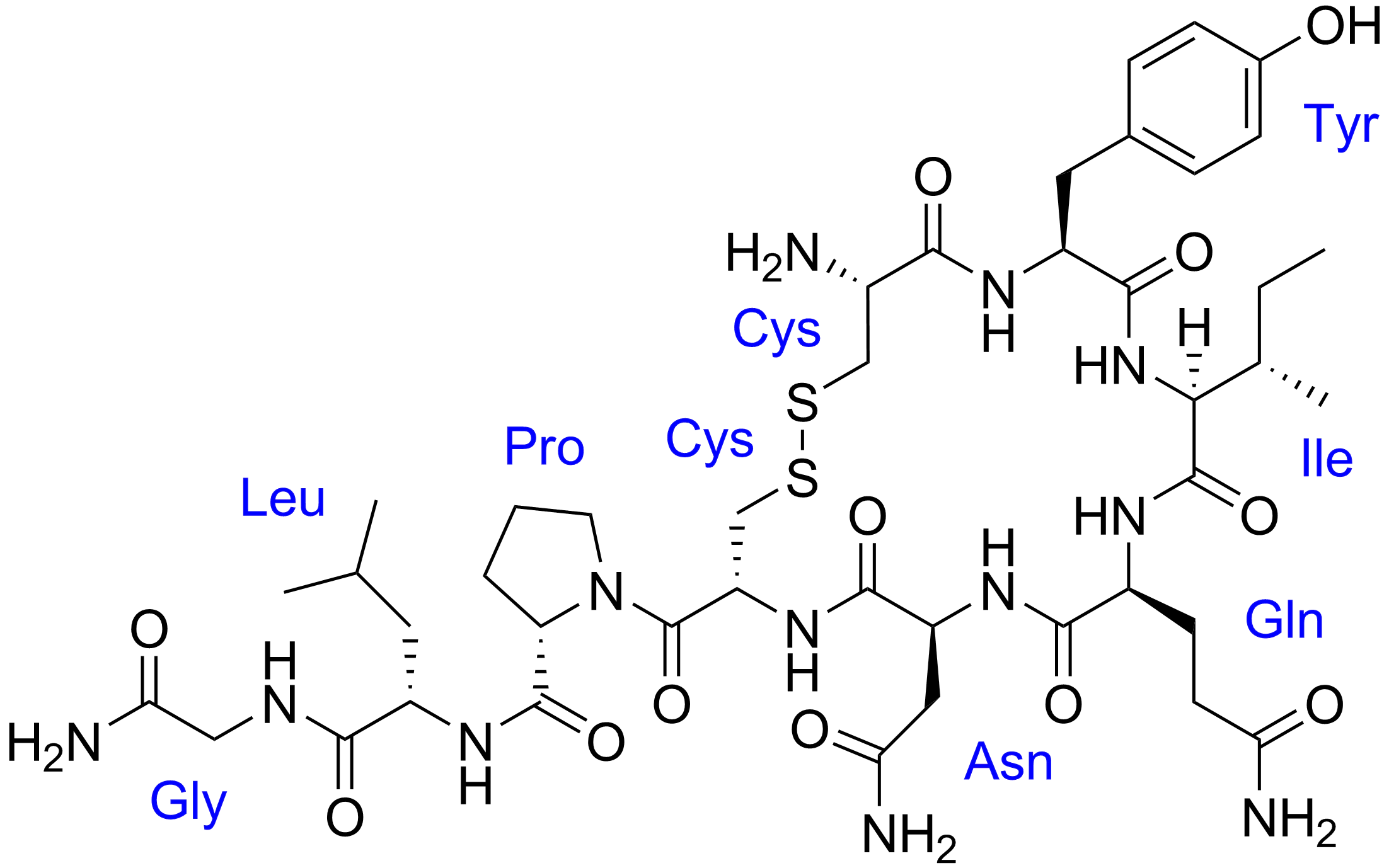
加强母亲和孩子之间的情感纽带
促进雌性哺乳动物分泌乳液
在分娩时导致宫缩
由海马体分泌, 作用于脑垂体
内啡肽
内啡肽是一类复杂的肽, 包括Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta四类
α内啡肽

- 由脑下垂体前叶的POMC(POMC,Proopiomelanocortin)前体蛋白通过酶切产生
Chem-BK
α-内啡肽具有一些重要的生理作用。它是内啡肽家族中最强的镇痛剂之一,可与、 和阿片受体结合,发挥镇痛作用。α-内啡肽还具有抗炎、抗压力和调节情绪的作用,能够提高人体的耐力和免疫功能。
β内啡肽
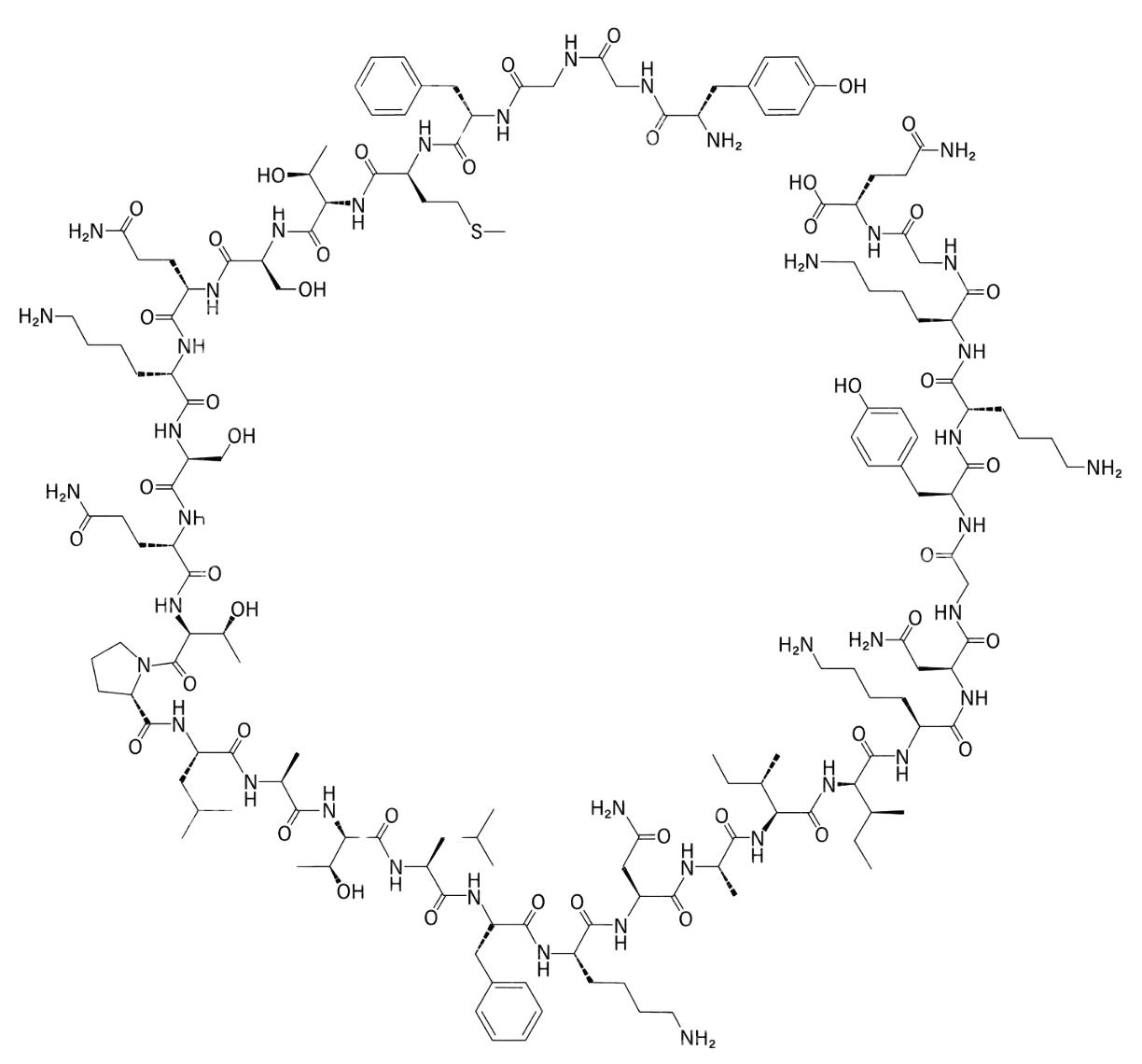
- 1977年从人体的垂体组织中发现
百度百科
已在神经系统、内分泌器官、消化道以及胎盘和羊水中均有-内啡肽及其前体蛋白存在。它具有很强的镇痛效应;能促进生长素、催乳素、生长抑素和胰高血糖素的释放等;应激时-内啡肽释放增多;可能是某些精神病发病的原因之一;其含量增高可促进脑缺血性脑水肿的形成;有抑制呼吸运动的频率和幅度的作用,并有报道认为它可能是肾脏的一种营养激素;对动物摄食行为有促进作用;与体温调节有关,并可视为免疫反应的生理调节因子,在中枢神经与免疫系统间起着体液传递介质的作用。
γ内啡肽
Wikipedia
Similar to other endorphins, research focusing upon γ-endorphin has been ongoing since its discovery in the 1970s. Yet, most of the information about the substance's exact role within the body is speculation that has yet to be proven. Some studies have indicated, however, that the polypeptide has antipsychotic effects on a certain category of patients with schizophrenia, while others suggest that γ-endorphin may act to help regulate blood pressure. Further research is needed, but if γ-endorphin does indeed possess such characteristics, the substance could eventually be utilized as a useful means of medical treatment.
δ内啡肽
氧化氮
脂溶性气体, 直接通过磷脂传播作用于细胞内分子
和自己有关
神经之间的信息传递 Informatics
大脑的发育 Development
大脑可塑性 Plasticity
大脑的老化 Aging
脑功能
感知功能 Sense
认知与记忆系统 Language
语言系统 Motor/Movement
睡眠系统 Sleep
应激反应 Stress
动机与情绪 Movitation and Emotion
脑疾病
儿童障碍性疾病 Childhood Disorder
上瘾 Addiction
精神疾病 Psychiatric Disorder
精神病学笔记请移步至这里